Belt In Car Engine – High-Quality Parts for Car Are Important
The belt in car engine is a critical component that ensures smooth and efficient operation of various systems, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Whether it’s a serpentine belt, timing belt, or V-belt, selecting the right belt for your vehicle is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent costly repairs. In this guide, we will explore the different types of belts used in car engines, their functions, and the factors to consider when choosing the best belt for your needs. By understanding these elements, you can make an informed decision and ensure your car runs reliably.
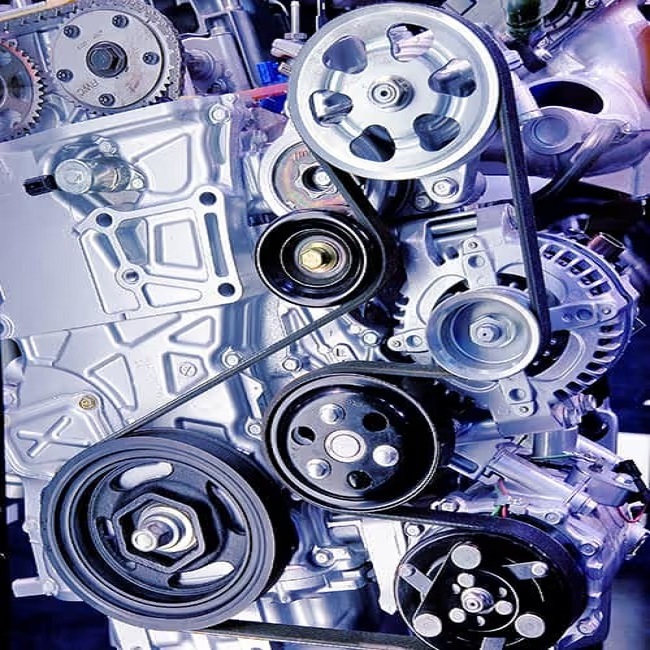

Understanding the Role of Belts in a Car Engine
Before diving into the selection process, it’s important to understand the primary roles of belts in a car engine:
Power Transmission
Belts transfer mechanical energy from the engine’s crankshaft to peripheral components such as the alternator, water pump, and air conditioning system. This ensures that all systems receive the necessary power to function correctly.
Synchronization (Timing Belts)
Timing belts synchronize the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring precise valve timing. A malfunctioning timing belt can lead to severe engine damage, making its proper selection crucial.
Durability and Reliability
A high-quality belt minimizes slippage, reduces wear on pulleys, and withstands extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. Choosing the right belt contributes to the longevity and reliability of your engine.
Types of Belts Used in Car Engines
There are several types of belts commonly found in car engines, each serving a specific purpose:
Serpentine Belts
- Function: Powers multiple accessories simultaneously, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
- Advantages: Compact design, easy maintenance, and ability to drive multiple components with a single belt.
- Disadvantages: If the belt fails, all connected systems stop functioning, which can leave you stranded.
Timing Belts
- Function: Ensures precise synchronization between the camshaft and crankshaft, controlling valve timing.
- Advantages: Quieter operation compared to timing chains; lighter weight.
- Disadvantages: Requires regular replacement (typically every 60,000–100,000 miles) to avoid catastrophic engine failure.
V-Belts
- Function: Transfers power to individual components like the alternator or water pump.
- Advantages: Simple design and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: Less efficient than serpentine belts; prone to slippage under heavy loads.
Poly-V Belts
- Function: Combines features of serpentine and V-belts, providing better grip and efficiency.
- Advantages: Improved performance and durability compared to traditional V-belts.
- Disadvantages: Higher cost than standard V-belts.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Belt
Selecting the right belt involves evaluating several key factors to ensure compatibility and performance:
Vehicle Specifications
- Always refer to your vehicle’s owner manual or service guide to determine the correct belt type, size, and specifications. Using the wrong belt can lead to improper fitment and potential engine damage.
Material Quality
- Look for belts made from high-quality materials such as reinforced rubber, polyester cords, or Kevlar fibers. These materials enhance durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion.
Brand Reputation
- Opt for reputable brands like Gates, Dayco, or Continental, which are known for producing reliable and long-lasting belts. Avoid low-cost alternatives that may compromise quality.
Environmental Conditions
- Consider the climate and driving conditions in your area. For example, if you live in a hot or humid region, choose a belt designed to withstand high temperatures and moisture exposure.
Load Requirements
- Evaluate the power demands of your engine’s accessories. High-performance engines or vehicles with aftermarket modifications may require belts with higher load capacities.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting the Right Belt
Follow these steps to ensure you choose the best belt for your car engine:
Identify the Belt Type
- Determine whether your vehicle uses a serpentine belt, timing belt, V-belt, or another type. Check the owner’s manual or consult a mechanic if unsure.
Measure the Belt Size
- Use a belt measuring tool or refer to the specifications in your vehicle’s manual. Pay attention to length, width, and rib count (for serpentine belts).
Inspect Existing Belts
- Examine the current belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or glazing. This will help you identify any issues that need addressing and confirm the correct replacement size.
Compare Options
- Research different brands and models based on reviews, warranties, and price. Compare features such as material composition, tensile strength, and temperature resistance.
Verify Compatibility
- Double-check that the selected belt matches your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Cross-reference part numbers with manufacturer databases if necessary.
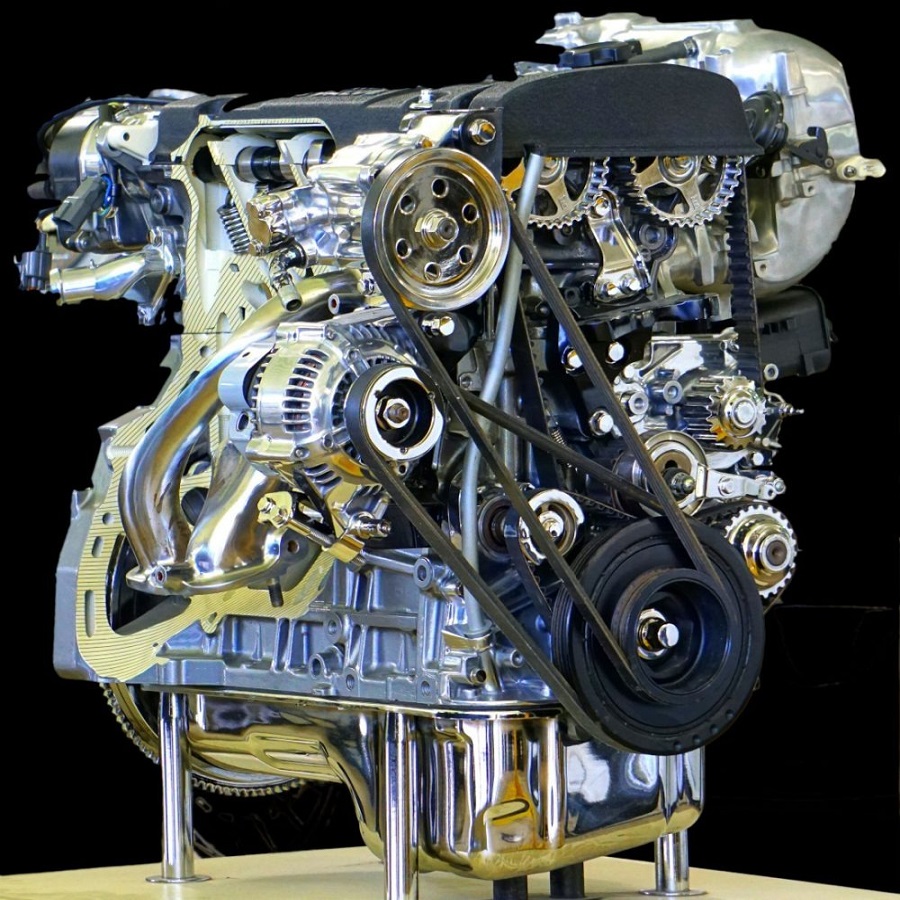

Signs That You Need to Replace Your Car Engine Belt
Knowing when to replace your belt is just as important as choosing the right one. Watch for these warning signs:
Visible Wear and Tear
- Cracks, splits, or frayed edges indicate that the belt is nearing the end of its lifespan.
Squealing Noises
- A high-pitched squeal during startup or acceleration often signals a loose or worn-out belt.
Reduced Performance
- Malfunctions in accessories like the alternator, power steering, or air conditioning may point to a failing belt.
Mileage Recommendations
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended replacement intervals, especially for timing belts, to avoid engine damage.
Oil or Coolant Leaks
- Contamination from leaks can degrade the belt material, necessitating immediate replacement.
Installation Tips for Car Engine Belts
Proper installation is crucial to ensure the belt performs optimally and lasts as long as possible:
Gather Tools and Supplies
- You’ll need basic tools such as wrenches, sockets, and a tension gauge. Ensure you have the correct replacement belt before starting.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
- Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for detailed instructions on removing and installing the belt.
Adjust Tension Properly
- Over-tightening or under-tightening the belt can cause premature wear or slippage. Use a tension gauge to achieve the recommended tension level.
Inspect Pulleys and Components
- While replacing the belt, inspect pulleys, idlers, and tensioners for signs of damage or misalignment. Replace any faulty parts to prevent future issues.
Test Drive After Installation
- Take a short test drive to ensure all systems are functioning correctly and there are no unusual noises or vibrations.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Belt Lifespan
Regular maintenance can significantly prolong the life of your car engine belt:
Regular Inspections
- Check the belt periodically for signs of wear, cracks, or contamination.
Keep It Clean
- Remove dirt, debris, and oil buildup from the belt and pulley surfaces to prevent slippage and premature wear.
Monitor Tension
- Ensure the belt remains properly tensioned to avoid excessive stress or slack.
Replace Related Components
- Replace worn pulleys, idlers, or tensioners during belt replacement to maintain overall system integrity.
Follow Service Intervals
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended service schedule for belt inspections and replacements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When selecting or installing a car engine belt, avoid these common pitfalls:
Ignoring Vehicle Specifications
- Using the wrong belt size or type can lead to poor performance and potential engine damage.
Neglecting Regular Inspections
- Failing to inspect the belt regularly increases the risk of sudden failure.
Cutting Corners on Quality
- Opting for cheaper, low-quality belts may save money initially but result in frequent replacements and potential breakdowns.
Improper Installation
- Incorrect tension or alignment during installation can shorten the belt’s lifespan and cause accessory malfunctions.
Conclusion: Ensuring Reliable Engine Performance
Choosing the right belt for your car engine is a vital step in maintaining its reliability and performance. By understanding the different types of belts, considering key factors like material quality and compatibility, and following proper installation and maintenance practices, you can ensure your engine operates smoothly for years to come. Remember, investing in a high-quality belt and adhering to regular maintenance schedules not only protects your vehicle but also provides peace of mind knowing that your engine is running efficiently. So take the time to select the best belt for your car—it’s a small investment that pays off in the long run.