What Is A Mid Engine Car? – Important Car Parts

What is a mid engine car? The automotive world is filled with innovations and designs that cater to different driving experiences, performance needs, and aesthetic preferences. Among these designs, the mid-engine car stands out as one of the most iconic and revered configurations in the industry. A mid-engine car is not just a vehicle; it’s an engineering marvel that combines balance, agility, and power in ways that few other layouts can achieve. From supercars like the Ferrari F8 Tributo to everyday sports cars like the Toyota MR2, mid-engine vehicles have captured the imagination of drivers and engineers alike.
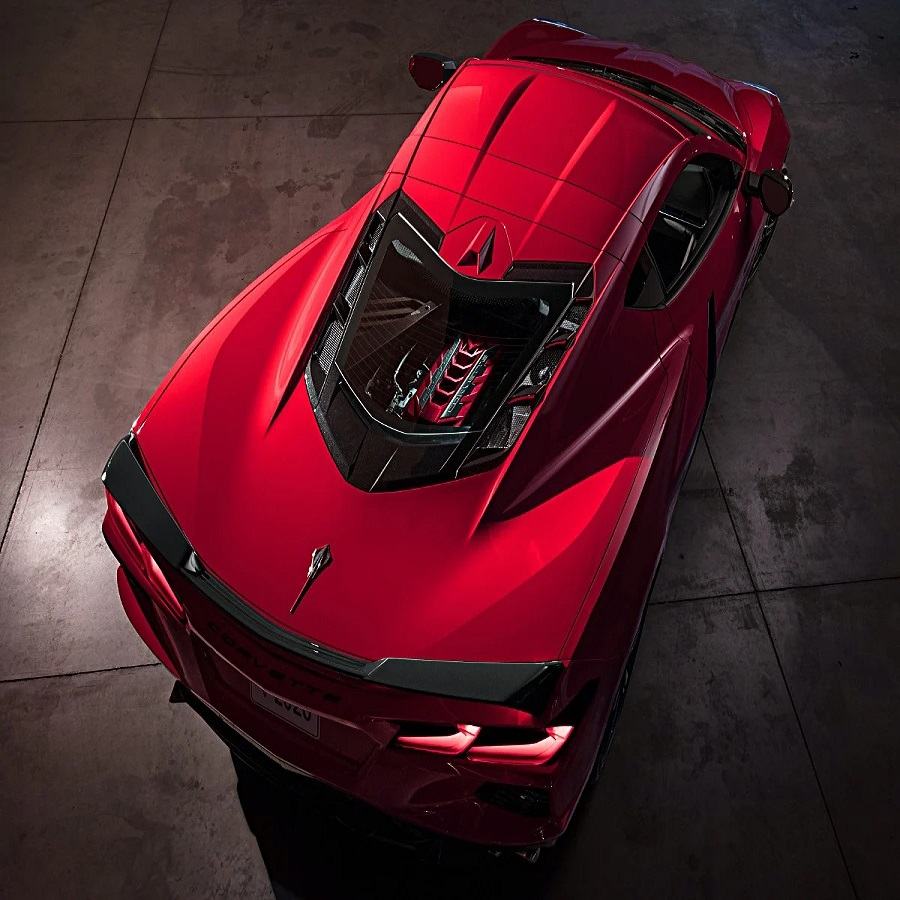

Defining the Mid-Engine Layout
What Makes a Car “Mid-Engine”?
A mid-engine car is defined by the placement of its engine between the front and rear axles, typically behind the driver but ahead of the rear wheels. This configuration places the engine closer to the center of the vehicle, optimizing weight distribution and enhancing handling characteristics. Unlike front-engine cars, where the engine sits over or in front of the front axle, or rear-engine cars, where the engine is located behind the rear axle, the mid-engine layout strikes a balance between the two extremes.
Key Characteristics
- Centralized Weight Distribution: The engine’s position near the center of the car ensures a more balanced weight distribution, which improves stability and cornering.
- Compact Design: Mid-engine cars often feature a shorter wheelbase and a lower center of gravity, contributing to their sporty appearance and dynamic performance.
- Rear-Wheel or All-Wheel Drive: Most mid-engine cars are designed with rear-wheel drive (RWD) or all-wheel drive (AWD), maximizing traction and control during acceleration.
The Advantages of a Mid-Engine Layout
Superior Handling and Balance
One of the primary benefits of a mid-engine car is its exceptional handling. By placing the engine near the center of the vehicle, the car achieves a near-perfect 50:50 weight distribution between the front and rear axles. This balance reduces understeer (a tendency for the front wheels to lose grip) and oversteer (a tendency for the rear wheels to slide), resulting in predictable and precise steering.
Enhanced Agility
Mid-engine cars are known for their agility and responsiveness. The centralized mass allows for quicker transitions during cornering, making them ideal for high-performance driving. Drivers can push the limits of the car without losing control, thanks to the balanced weight distribution and low center of gravity.
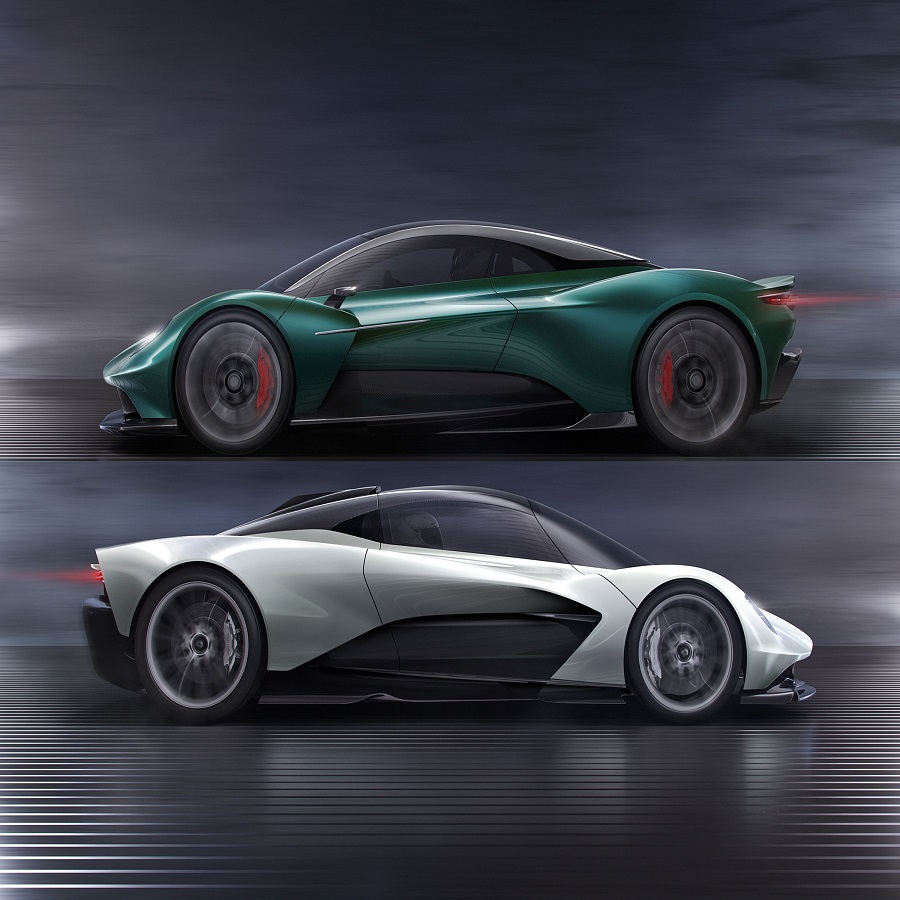

Improved Acceleration
With the engine positioned close to the driven wheels (usually the rear wheels), mid-engine cars benefit from superior traction during acceleration. This setup minimizes wheel spin and maximizes power delivery, allowing for rapid launches and impressive acceleration figures.
Aesthetic Appeal
Beyond performance, mid-engine cars are visually striking. Their unique proportions—short front ends, elongated cabins, and muscular rear sections—create a distinctive silhouette that sets them apart from traditional front-engine vehicles. This design language has become synonymous with exotic sports cars and supercars.
The Disadvantages of a Mid-Engine Layout
Limited Practicality
While mid-engine cars excel in performance, they often fall short in practicality. The engine’s placement consumes valuable space that could otherwise be used for passenger seating or cargo storage. As a result, many mid-engine cars offer cramped interiors and minimal trunk space, making them less suitable for daily use.
Higher Cost of Ownership
Mid-engine cars are typically more expensive to purchase and maintain than their front-engine counterparts. The complex engineering required to package the engine, drivetrain, and cooling systems in such a confined space drives up production costs. Additionally, repairs and maintenance can be costly due to the specialized nature of these vehicles.
Reduced Crash Safety
Placing the engine behind the driver increases the risk of injury in rear-end collisions. While modern safety technologies have mitigated some of these concerns, mid-engine cars still face challenges in meeting stringent crash-test standards compared to front-engine vehicles.
Complex Cooling Systems
The mid-engine layout poses unique challenges for engine cooling. With limited airflow reaching the engine compartment, manufacturers must design sophisticated cooling systems to prevent overheating. This complexity adds weight and cost to the vehicle.
The History of Mid-Engine Cars
Early Innovations
The concept of the mid-engine layout dates back to the early days of motorsport. In the 1920s and 1930s, racing teams experimented with placing the engine behind the driver to improve handling and performance. One of the earliest examples was the Auto Union Type C Grand Prix car, designed by Ferdinand Porsche, which featured a mid-mounted V16 engine.
The Rise of Mid-Engine Supercars
The mid-engine configuration gained widespread recognition in the 1960s with the introduction of iconic models like the Lamborghini Miura and the Ford GT40. These cars demonstrated the potential of mid-engine design in both road and race applications, setting the stage for future innovations.
Modern Developments
Today, the mid-engine layout is synonymous with high-performance sports cars and supercars. Brands like Ferrari, McLaren, and Porsche continue to refine the design, incorporating advanced materials, hybrid powertrains, and cutting-edge aerodynamics. Even mainstream manufacturers like Chevrolet have embraced the mid-engine layout with the Corvette C8, marking a significant shift in the industry.
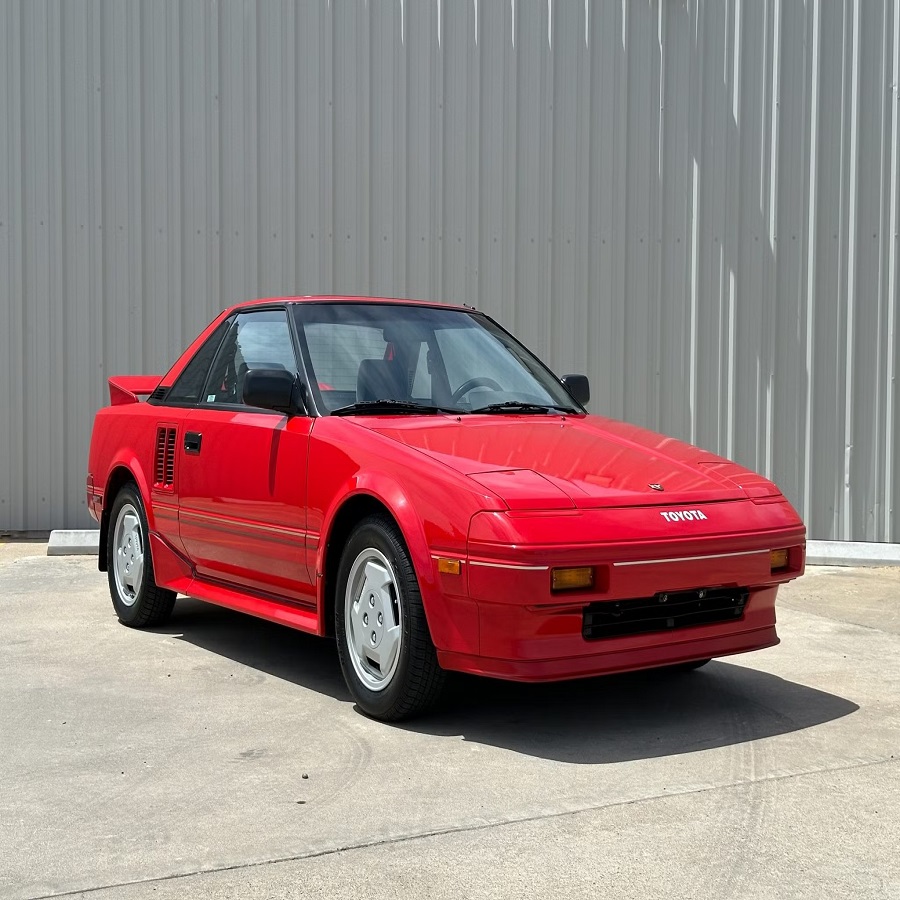

Notable Examples of Mid-Engine Cars
Supercars
- Ferrari F8 Tributo: A masterpiece of Italian engineering, the F8 Tributo combines a mid-mounted V8 engine with stunning design and razor-sharp handling.
- McLaren 720S: Known for its lightweight construction and incredible performance, the 720S exemplifies the modern mid-engine supercar.
- Porsche 911 GT3 RS: While the 911 series traditionally features a rear-engine layout, the GT3 RS incorporates mid-engine principles to enhance track performance.
Sports Cars
- Toyota MR2: A budget-friendly option, the MR2 brought mid-engine dynamics to the masses with its compact size and reliable performance.
- Lotus Elise: Renowned for its minimalist design and exceptional handling, the Elise showcases the purity of mid-engine engineering.
- Chevrolet Corvette C8: The first mid-engine Corvette, the C8 represents a bold departure from tradition and redefines American performance.
Racing Legends
- Ford GT40: A legendary race car that dominated the 24 Hours of Le Mans in the 1960s, the GT40 proved the superiority of the mid-engine layout in endurance racing.
- Porsche 917: Another Le Mans icon, the 917 combined a mid-engine configuration with raw power to achieve unparalleled success on the track.
The Impact of Mid-Engine Cars on the Automotive Industry
Pushing Technological Boundaries
Mid-engine cars have consistently pushed the boundaries of automotive technology. From advanced aerodynamics to hybrid powertrains, these vehicles serve as testbeds for innovations that eventually trickle down to mainstream models.
Inspiring Future Designs
The success of mid-engine cars has inspired manufacturers to rethink traditional layouts. For example, the transition of the Corvette to a mid-engine platform reflects a broader trend toward adopting this configuration for enhanced performance and appeal.
Cultural Significance
Mid-engine cars hold a special place in automotive culture. They represent the pinnacle of engineering excellence and embody the spirit of speed and adventure. From Hollywood blockbusters to video games, these vehicles have become symbols of aspiration and excitement.

Conclusion: The Legacy of Mid-Engine Cars
The mid-engine car is more than just a type of vehicle—it’s a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of perfection. By placing the engine at the heart of the car, manufacturers have created machines that deliver unparalleled performance, balance, and style. While mid-engine cars may not be the most practical choice for everyday driving, their impact on the automotive industry is undeniable.
From their origins in motorsport to their dominance in the supercar segment. Mid-engine cars continue to captivate enthusiasts and redefine. What’s possible in automotive design. As technology evolves, we can expect even more exciting developments in this iconic layout. Ensuring that the legacy of mid-engine cars endures for generations to come. Whether you’re a fan of roaring V12s or sleek hybrids. There’s no denying the allure of a well-engineered mid-engine machine.